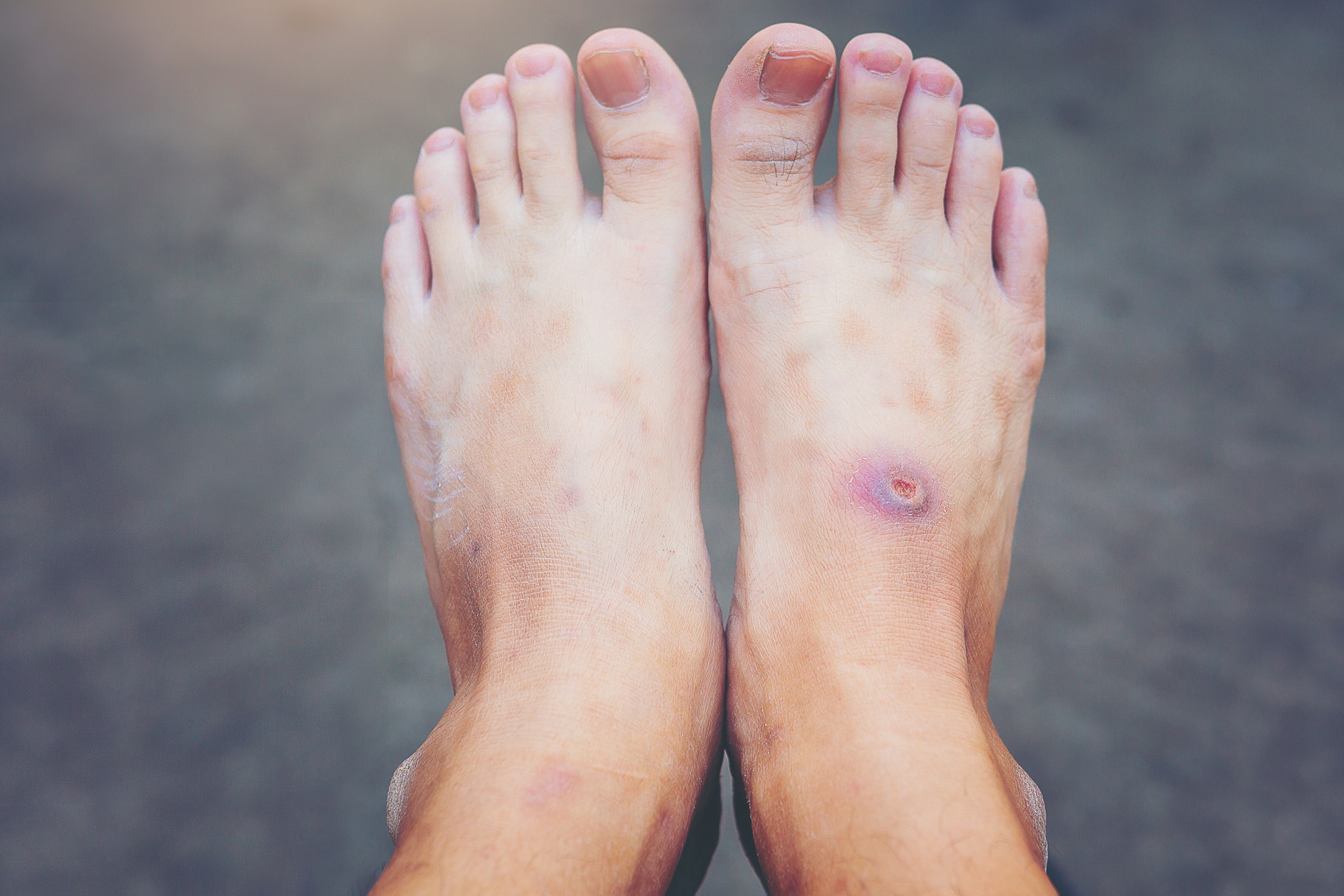
Understanding Gangrene in Diabetic Foot
Gangrene occurs when body tissues die due to a loss of blood supply. In diabetics, high blood sugar levels can lead to nerve damage and poor circulation. Gangrene in diabetic foot may manifest as dry, wet, or gas gangrene.
- Dry gangrene results from reduced blood flow and is often associated with diabetes.
- Wet gangrene, on the other hand, involves an infection that exacerbates the tissue damage.
- Gas gangrene is caused by bacteria infecting an area deprived of blood flow, and it rapidly progresses.
Visual illustrations often help in comprehending these types better. Recent statistics indicate an increase in diabetic foot conditions in India, emphasizing prevention and early care.
Identifying Signs and Symptoms
Identifying symptoms is imperative for early treatment. Warning signs of gangrene in diabetic foot include:
- Discoloration of the skin;
- Swelling or a clear fluid-filled blister;
- Pain that feels different from usual and is not relieved by rest.
Particularly for gangrene, one might note Nausea, fever, or even an unpleasant odor. Such symptoms should not be ignored. Real-life cases in India highlight the gravity of ignoring these signs. Timely attention and care can transform patient outcomes dramatically.
The Role of Early Detection
Timely diagnosis of gangrene in diabetic foot can avoid severe complications. Early intervention leads to better treatment outcomes and possibly, saves the foot. Easy steps for regular self-examination include:
- Inspecting feet daily for cuts, blisters, or color changes.
- Checking the temperature difference between both feet.
- Keeping an eye on toenails for fungal infections.
Family members can assist in these examinations, providing another layer of defense against complications. Empowering caretakers with this knowledge is crucial.
Key Prevention Strategies
Preventing gangrene in diabetic foot involves consistent care. Some effective strategies include:
- Foot Care: Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are essential.
- Footwear: Choose comfortable shoes that allow air circulation, reducing the risk of infections.
- Nutrition: A balanced diet helps maintain blood sugar levels, essential for foot health.
Adopting these habits can vastly reduce risks and ensure the well-being of diabetic patients.
Treatment Options Available
When prevention isn’t enough, understanding treatments for gangrene in diabetic foot is vital. In India, both medical and surgical options exist. These might include antibiotics for infections or surgery to remove dead tissue. Emerging technologies enhance treatment efficacy. Additionally, some patients explore traditional remedies. However, one should consult healthcare professionals to determine what’s best.
Understanding Accessibility and Affordability of Treatment
Accessibility and affordability remain challenges. India’s government initiatives strive to make healthcare more accessible. NGOs contribute significantly by offering support and resources for gangrene in diabetic foot care. However, disparities in urban versus rural access remain. Tailored programs aim to bridge this gap, ensuring equitable healthcare distribution.
Lifestyle Modifications to Support Prevention
Healthy lifestyle changes support foot health. Exercises improving circulation aid in preventing gangrene in diabetic foot. Practicing stress management can keep diabetes in check, supporting overall health. Community initiatives promote these healthy lifestyle changes, providing collective benefits and support.
Creating Awareness and Educating the Public
Awareness campaigns play vital roles in prevention. Partnering with healthcare providers extends the reach of education efforts, particularly within communities. Digital platforms provide vast opportunities to spread vital information about gangrene in diabetic foot, reaching millions.
Conclusion
Being proactive in prevention strategies against gangrene in diabetic foot is wise. Understanding risks and taking preventive measures empowers diabetic patients and their families. By participating in awareness initiatives and adopting healthy habits, the community steps forward towards better health outcomes.